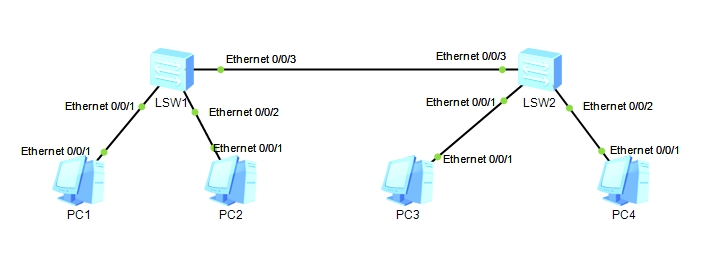
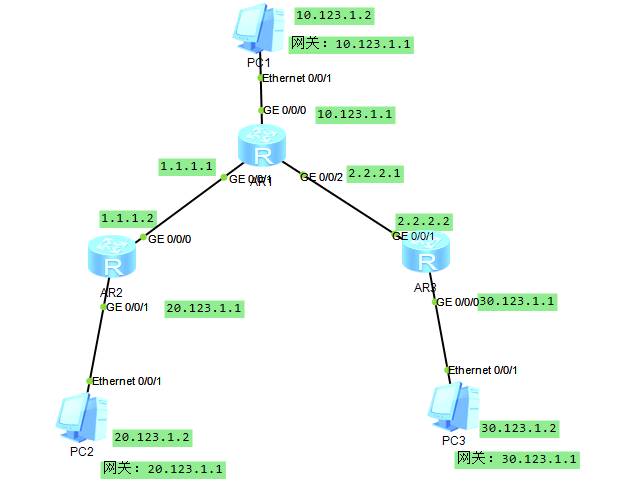
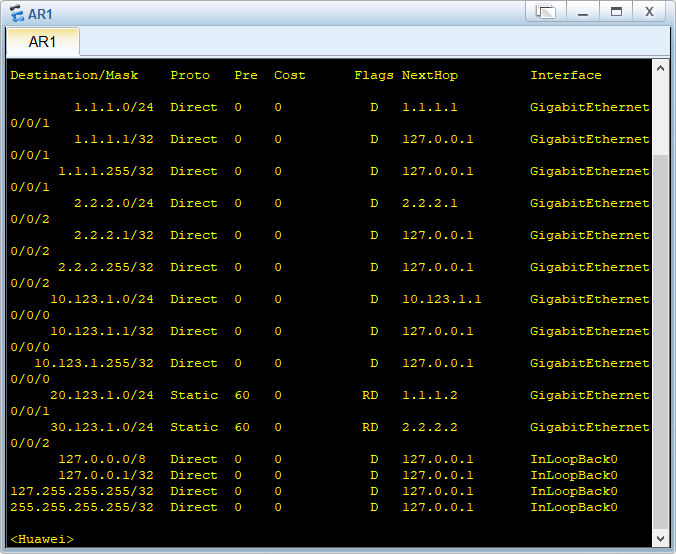
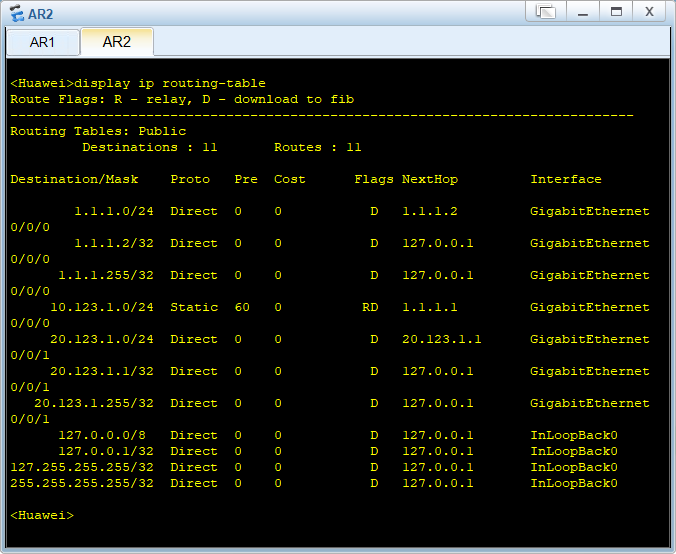
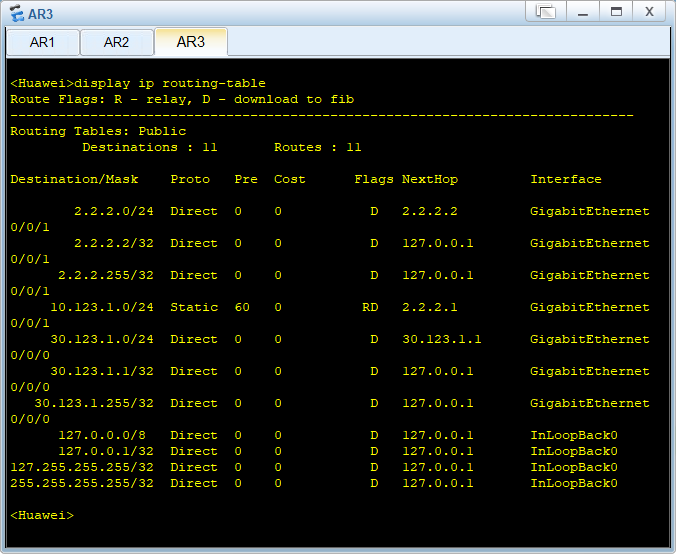
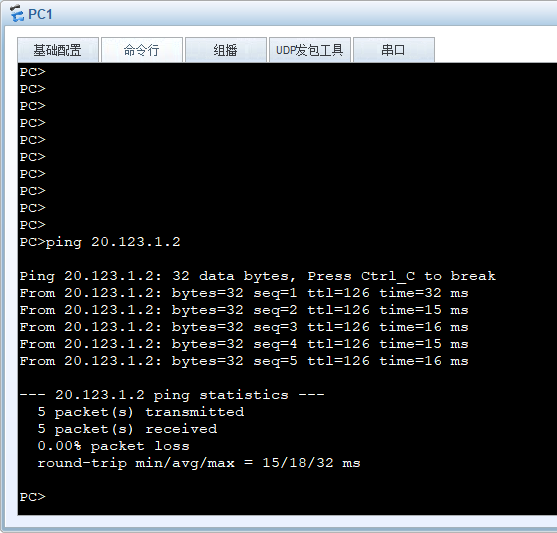
BGP路由优选实验组网

R2、R3、R4各添加Loopback0 接口
10.123.x.x
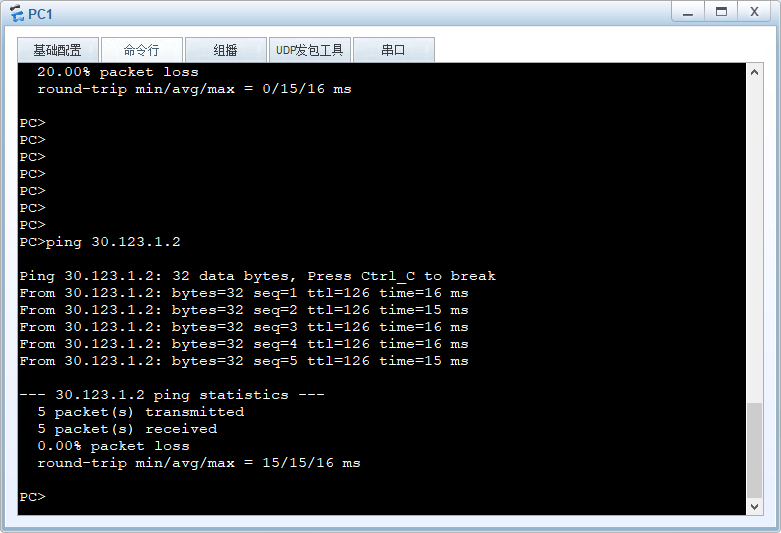
测试R2、R4的连通性


配置OSPF 64512
//配置R2,激活OSPF
[R2]ospf 1 router-id 10.123.2.2
[R2-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[R2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.123.2.2 0.0.0.0
[R2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.123.23.2 0.0.0.0
[R2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[R2-ospf-1] quit
//配置R3.激活OSPF
[R3]ospf 1 router-id 10.123.3.3
[R3-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[R3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.123.3.3 0.0.0.0
[R3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.123.23.3 0.0.0.0
[R3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.123.34.3 0.0.0.0
[R3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[R3-ospf-1] quit
//配置R4,激活OSPF
[R4]ospf 1 router-id 10.123.4.4
[R4-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[R4-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.123.4.4 0.0.0.0
[R4-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.123.34.4 0.0.0.0
[R4-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[R4-ospf-1] quit
在R3查看ospf的邻居信息

查看OSPF路由表

配置BGP对等体
//配置R1
[R1]bgp 100
[R1-bgp] router-id 10.123.1.1
[R1-bgp] peer 10.123.12.2 as 64512
//配置R2
[R2]bgp 64512
[R2-bgp] router-id 10.123.2.2
[R2-bgp] peer 10.123.3.3 as-number 64512
[R2-bgp] peer 10.123.3.3 connect-interface LoopBack0
[R2-bgp] peer 10.123.3.3 next-hop-local
[R2-bgp] peer 10.123.12.1 as-number 100
//配置R3
[R3]bgp 64512
[R3-bgp] router-id 10.123.3.3
[R3-bgp] peer 10.123.2.2 as-number 64512
[R3-bgp] peer 10.123.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack0
[R3-bgp] peer 10.123.4.4 as-number 64512
[R3-bgp] peer 10.123.4.4 connect-interface LoopBack0
//配置R4
[R4]bgp 64512
[R4-bgp] router-id 10.123.4.4
[R4-bgp] peer 10.123.3.3 as-number 64512
[R4-bgp] peer 10.123.3.3 connect-interface LoopBack0
[R4-bgp] peer 10.123.3.3 next-hop-local
[R4-bgp] peer 10.123.45.5 as-number 200
//配置R5
[R5]bgp 200
[R5-bgp] router-id 10.123.5.5
[R5-bgp] peer 10.123.45.4 as 64512
在R2、R4上检查BGP对等体状态


路由发布到BGP中
//R1
[R1]bgp 100
[R1-bgp] network 172.16.1.0 24
[R1-bgp] network 172.16.2.0 24
[R1-bgp] network 172.16.3.0 24
[R1-bgp] network 172.16.4.0 24
//R5
[R5]bgp 200
[R5-bgp] network 172.16.1.0 24
[R5-bgp] network 172.16.2.0 24
[R5-bgp] network 172.16.3.0 24
[R5-bgp] network 172.16.4.0 24
查看R3的路由表,查看BGP是否学习

修改AS_Path属性
//创建IP前缀列表1,匹配Loopback1接口路由
[R1]ip ip-prefix 1 permit 172.16.1.0 24 greater-equal 24 less-equal 24
//创建Route-Policy hcip,并创建节点10,在其中调用IP前缀列表1,修改AS_Path属性值
[R1]route-policy hcip permit node 10
[R1-route-policy] if-match ip-prefix 1
[R1-route-policy] apply as-path 300 400 additive
[R1-route-policy] quit
[R1]route-policy hcip permit node 20
//对向BGP对等体R2通告的BGP路由应用Route-Policy
[R1]bgp 100
[R1-bgp] peer 10.0.12.2 route-policy hcip export
//在R1上触发出方向的软复位,刷新对外通告的BGP路由
<R1>refresh bgp all export
在R3上查看BGP路由172.16.1.0/24的信息

此时R3优选R4通告的BGP路由172.16.1.0/24,R2通告的未被优选的原因是AS_Path长度。
修改Local_Preference属性
创建IP前缀列表1,匹配BGP路由172.16.2.0/24
[R4]ip ip-prefix 1 permit 172.16.2.0 24 greater-equal 24 less-equal 24

创建Route-Policy hcip,并创建节点10,在其中调用IP前缀列表1,修改Local_Preference属性值
[R4]route-policy hcip permit node 10
[R4-route-policy] if-match ip-prefix 1
[R4-route-policy] apply local-preference 200
[R4-route-policy] quit
[R4]route-policy hcip permit node 20

对向BGP对等体R3通告的BGP路由应用Route-Policy
[R4]bgp 64512
[R4-bgp] peer 10.0.3.3 route-policy hcip export

刷新对外通告BGP路由
<R4>refresh bgp all export
在R3上查看BGP路由172.16.2.0/24的明细信息

此时R3优选R4通告的BGP路由172.16.2.0/24,R2通告的BGP路由其Local_Preference值为100,小于R3通告的BGP路由Local_Preference值200,因此R2通告的BGP路由未被优选。
修改MED属性
在R2上使得R3优选R5发布的BGP路由172.16.3.0/24
//ip前缀列表1 匹配GBP路由172.16.3.0/24
[R2]ip ip-prefix 1 permit 172.16.3.0 24 greater-equal 24 less-equal 24
创建Route-Policy hcip,并创建节点10,在其中调用IP前缀列表1,修改MED属性值
[R2]route-policy hcip permit node 10
[R2-route-policy] if-match ip-prefix 1
[R2-route-policy] apply cost 200
[R2-route-policy] quit
[R2]route-policy hcip permit node 20
对来自BGP对等体R1的BGP路由应用Route-Policy
[R2]bgp 64512
[R2-bgp] peer 10.0.12.1 route-policy hcip import
在R2刷新接收到的BGP路由
<R2>refresh bgp all import
在R3上配置允许来自不同AS的BGP路由的MED值
[R3]bgp 64512
[R3-bgp] compare-different-as-med
在R3上查看BGP路由172.16.3.0/24的明细信息

R2通告的BGP路由172.16.3.0/24其MED值为200,而R4通告BGP路由MED值为0,R3优选MED值较小的BGP路由,因此R2通告的BGP路由未被优选。
修改preferred-value属性
修改R3的路由的pre-value属性的策略,使得R3优选R4通告的BGP路由172.16.4.0/24
创建IP前缀列表1,匹配BGP路由172.16.4.0/24
[R3]ip ip-prefix 1 permit 172.16.4.0 24 greater-equal 24 less-equal 24
创建Route-Policy hcip,并创建节点10,在其中调用IP前缀列表1,修改preferred-value属性值
[R3]route-policy hcip permit node 10
[R3-route-policy] if-match ip-prefix 1
[R3-route-policy] apply preferred-value 300
[R3-route-policy] quit
[R3]route-policy hcip permit node 20
对来自BGP对等体R4的BGP路由应用Route-Policy
[R3]bgp 64512
[R3-bgp] peer 10.123.4.4 route-policy hcip import
R3刷新收到的路由并查看BGP路由172.16.4.0/24的信息

R4通告的BGP路由172.16.3.0/24其preferred-value值为300,而R2通告的preferred-value值为0,R3优选preferred-value值较大的BGP路由,因此R3优选R4通告的BGP路由。
修改Origin属性
在R1、R5上创建Loopback5接口,将接口路由发布到BGP中,验证Origin属性为IGP的BGP路由优于Origin属性为Incomplete的BGP路由。
R1、R5上创建Loopback5,IP地址为172.16.5.1/24
[R1]interface LoopBack 5
[R1-LoopBack5] ip address 172.16.5.1 24
[R1-LoopBack5] quit
[R5]interface LoopBack 5
[R5-LoopBack5] ip address 172.16.5.1 24
[R5-LoopBack5] quit
在R1、R5上将Loopback5接口路由发布到BGP中,通过network方式
[R1]bgp 100
[R1-bgp] network 172.16.5.0 24
[R5]bgp 200
[R5-bgp] network 172.16.5.0 24
在R3上查看BGP路由表

此时R3上优选R2通告(由R1发布)的BGP路由172.16.5.0/24,此时R2、R4通告的BGP路由Origin属性值都为IGP。
在R1上取消将Loopback5接口路由发布到BGP

创建IP前缀列表2,匹配R1 Loopback5接口路由172.16.5.0/24
[R1]ip ip-prefix 2 permit 172.16.5.0 24 greater-equal 24 less-equal 24

创建Route-Policy origin,并创建节点10,在其中调用IP前缀列表2
[R1]route-policy origin permit node 10
[R1-route-policy] if-match ip-prefix 2
[R1-route-policy] quit

R1上修改为使用import-route direct将直连路由发布到BGP,调用Route-Policy origin限制只引入Loopback5接口路由
[R1]bgp 100
[R1-bgp] import-route direct route-policy origin

在R3上查看BGP路由172.16.5.0/24的明细信息

此时R3优选R4通告的BGP路由172.16.5.0/24。
R2通告(R1发布)的BGP路由172.16.5.0/24此时Origin属性值为incomplete(通过import-route方式发布到BGP),由于Origin属性值原因,该条路由未被优选。
验证BGP优选到Nex_Hop的IGP度量值最小的路由
R2、R4之间基于环回口建立IBGP对等体关系,在R2、R3上建立Loopback7接口并将接口路由发布到BGP中,在R4上观察BGP路由优选情况。
R2、R4之间建立IBGP对等体关系
[R2]bgp 64512
[R2-bgp] peer 10.0.4.4 as-number 64512
[R2-bgp] peer 10.0.4.4 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[R4]bgp 64512
[R4-bgp] peer 10.0.2.2 as-number 64512
[R4-bgp] peer 10.0.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack0
检查IBGP对等体关系状态

R2、R4上创建Loopback7接口,并将接口路由发布到BGP
[R2]interface LoopBack 7
[R2-LoopBack7] ip address 172.16.7.1 24
[R2-LoopBack7] quit
[R2]bgp 64512
[R2-bgp] network 172.16.7.0 24
[R3]interface LoopBack 7
[R3-LoopBack7] ip address 172.16.7.1 24
[R3-LoopBack7] quit
[R3]bgp 64512
[R3-bgp] network 172.16.7.0 24
在R4上查看BGP路由172.16.7.0/24的明细信息

R4优选R3发布的BGP路由,其IGP cost为1,小于R2发布的BGP路由IGP cost 2。
R2发布的BGP路由未被优选的原因为IGP cost。
]]>